Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
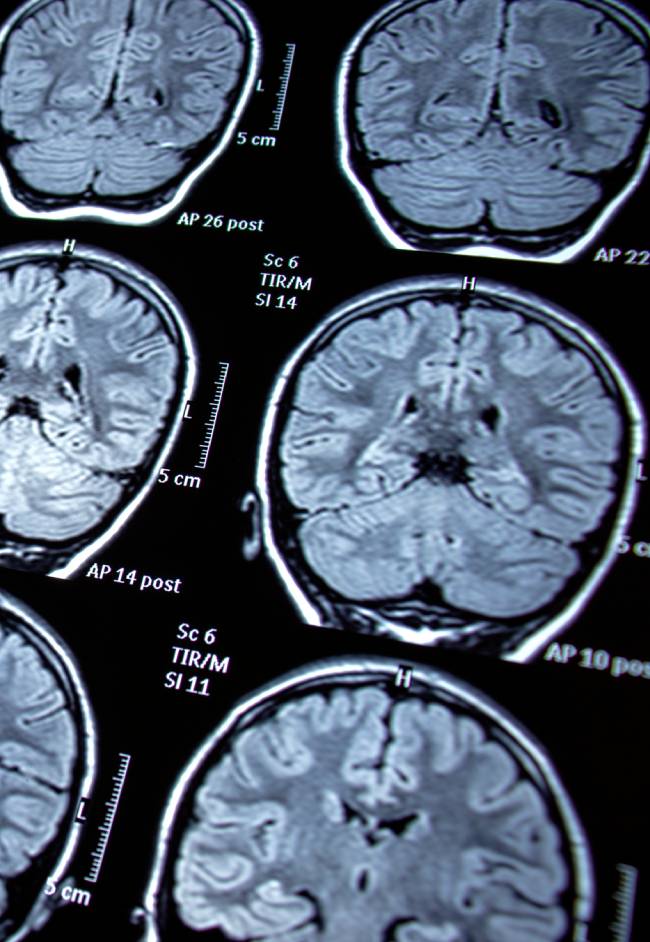
An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels in the brain where arteries connect directly to veins, bypassing normal capillary pathways. An AVM can disrupt normal blood flow and oxygen delivery and increase the risk of bleeding, seizures, and neurological symptoms. Some AVMs cause headaches, weakness, vision problems, or speech changes, while others remain silent until they rupture and become a medical emergency.
Treatment Options
Diagnosis is typically made through MRI, CT angiography, or cerebral angiography. The right type of imaging will depend on your situation, symptoms, and medical history. Treatment depends on the AVM’s size, location, and risk factors, and may include surgical removal, stereotactic radiosurgery, or endovascular embolization.
