Intracerebral Hemorrhage
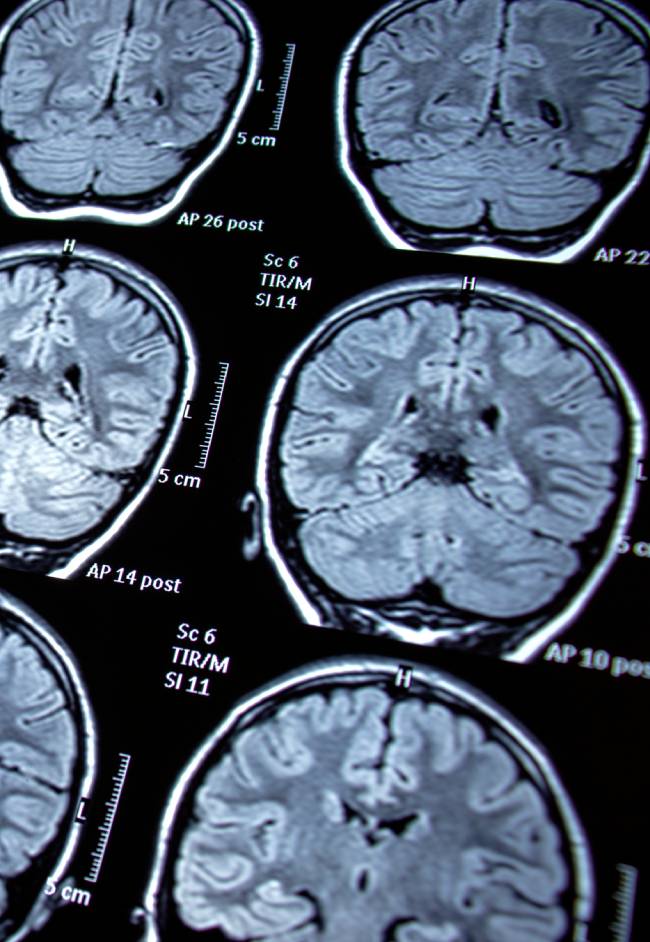
An intracerebral hemorrhage is a form of stroke caused by bleeding directly into the brain tissue. When a blood vessel within the brain bursts, the hemorrhage starts. It leads to pressure, swelling, and damage to surrounding brain cells. Common causes include high blood pressure, head trauma, blood vessel abnormalities (like aneurysms for example), and blood-thinning medications. Symptoms can include severe headache, weakness or numbness (especially on one side), confusion, difficulty speaking, vision problems, and loss of coordination or consciousness. Diagnosis is typically made using a CT scan or MRI to visualize the bleeding.
Treatment
Depending on the severity of the hemorrhage, treatment can include medications to control blood pressure levels, reduce swelling, or reverse blood thinners. Surgery is needed in some cases to drain the blood or relieve pressure. Recovery varies and often involves rehabilitation to regain lost functions.
